Table of Contents
- 1. What is SSH?
- 2. SSH in Linux servers
- 3.
- 4. How to log into Linux server via SSH
- 5. 1. Login from Windows
- 6.
- 7. 2. Login from Linux/macOS
- 8. 3. Login with SSH Key
- 9. Common SSH commands
- 10. Troubleshooting common errors
- 11. Permission denied
- 12. Connection refused
- 13. Host key verification failed
- 14. Connection timeout
- 15. SSH Security
- 16. Conclusion
What is SSH?
SSH (short for Secure Socket Shell) is a network protocol used to log into a remote computer. For example, if you have a Linux computer at home with SSH installed, you can log into that computer remotely to manage data. All data that you send or receive through the SSH protocol is encrypted to ensure safer information security.
SSH in Linux servers
When you purchase a Linux VPS or a physical server running Linux, you will receive login information through the SSH protocol including:
- Server IP
- Login username, mostly root
- User password, if your username is root then this password is called root password
- Communication port: 22, SSH uses port 22 by default
With that information, you can already log into your Linux server.
How to log into Linux server via SSH
1. Login from Windows
Using PuTTY:
- Download PuTTY from putty.org
- Open PuTTY, enter server IP in the "Host Name" field
- Keep Port 22 (or change if server uses a different port)
- Click "Open" to connect
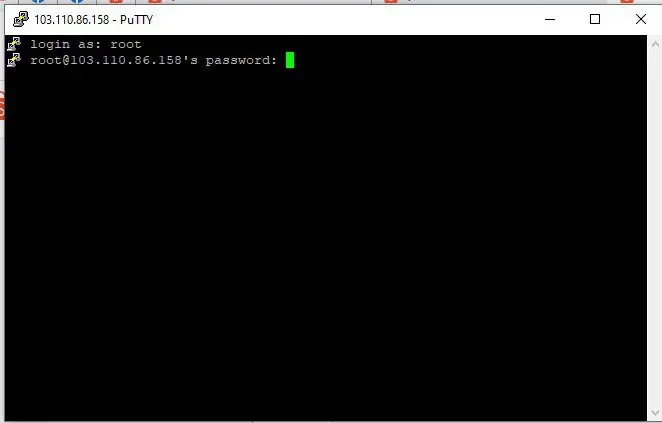
- Enter username when prompted
- Enter password (not displayed when typing)
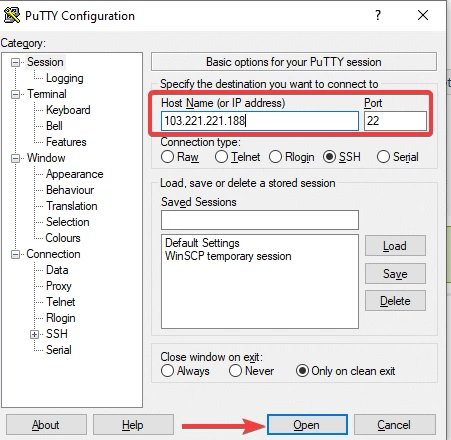
The red circled line is where you enter the server IP address, default port is 22, only modify if you're sure your server uses a different network port.
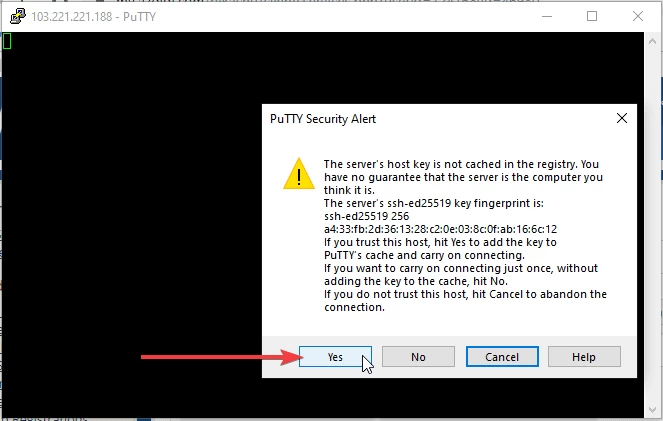
Note: when entering in the window, the password is not displayed. You just need to enter the correct and complete password then press Enter to connect.
Additionally, for convenience you can copy the password then right-click on the PuTTY screen to paste that password, then press Enter as usual.
Using Windows Terminal or PowerShell: Windows 10 and above has OpenSSH integrated. Open Terminal or PowerShell and type:
ssh username@ip_serverVí dụ: ssh [email protected]
2. Login from Linux/macOS
If you use Linux or macOS operating systems, the machine already has the Terminal tool that can run Unix commands. In Terminal, you use the following command to log in:
ssh [email protected]Where root is the username on the server and 123.45.67.8 is the server's IP address. If you use a network port other than port 22, you'll need to declare the port number with the -p parameter. If you use SSH Key, you can refer to the following article.
ssh [email protected] -p 22223. Login with SSH Key
SSH Key is more secure than password and doesn't require entering password each time you log in.
Create SSH Key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096Copy public key to server:
ssh-copy-id username@ip_serverLogin with SSH Key:
ssh -i /path/to/private_key username@ip_serverCommon SSH commands
- Login with specific user: ssh user@ip_server
- Specify port: ssh -p 2222 user@ip_server
- Use key file: ssh -i keyfile.pem user@ip_server
- Enable verbose mode for debugging: ssh -v user@ip_server
- Port forwarding: ssh -L 8080:localhost:80 user@ip_server
Troubleshooting common errors
Permission denied
- Check username and password again
- Ensure account is not locked
- Check /etc/ssh/sshd_config file on server
Connection refused
- Check if server IP is correct
- Check if firewall is blocking SSH port
- Ensure SSH service is running on server
Host key verification failed
- Remove old key: ssh-keygen -R ip_server
- Reconnect and accept new key
Connection timeout
- Check network connection
- Check ISP firewall
- Try using VPN if blocked
SSH Security
- Change default port: Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config, change Port 22 to another number
- Disable root login: Set PermitRootLogin no in sshd_config
- Use SSH Key instead of password: Set PasswordAuthentication no
- Limit allowed connection IPs: Use firewall or TCP Wrapper
- Install Fail2Ban: Automatically block IP after multiple failed login attempts
- Use SSH Key passphrase: Add security layer for private key
Conclusion
SSH is an indispensable tool when managing Linux VPS. Mastering SSH login operations and security will help you work more efficiently and safely. Always remember to apply basic security measures such as using SSH Key, changing default port, and updating regularly to protect your server from threats.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt




Leave a comment